CoolWallet supports Polygon (MATIC), the token used for settling payments and transaction fees on the Polygon network, a sidechain (and sister chain) of the Ethereum network. Read the story behind Polygon and Ethereum problems they’re trying to solve.
What is Polygon (MATIC)?
Polygon is a layer 2 scaling solution on the Ethereum network. While it exists alongside the original chain, it creates a separate chain that is faster, maintains higher TPS (transactions per second), and lowers fees per transaction.
Crypto industries like GameFi, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized finance (DeFi) activities can often generate a very large number of small transactions, making Polygon and other layer 2s a solution to the scaling issues blockchains encounter when they become too congested and expensive to operate on.
Layer 2s allow developers and builders to bridge their assets to another blockchain and interact without volatile transaction fees affecting their decentralized application’s (dApps) ability to operate or conduct business with their users.
Polygon also offers staking to incentivize holding their tokens and reward users for helping secure the network.
Who is behind Polygon Finance?
Polygon was founded by Jaynti Kanani, Anurag Arjun, and Sandeep Nailwal in 2017. It held an Initial Exchange Offering (IEO) on the Binance Launchpad and have since received enormous investments from well-known venture capitalists and investors, including Sequoia Capital, Steadview Capital, and Mark Cuban.
Originally called Matic network, Polygon rebranded itself in February 2021 after a stagnant crypto winter period to appeal to a more global audience. At the same time it announced the rebranding, Polygon expanded its original plan to include interoperability with other chains, similar to Polkadot.
Polygon chose to keep MATIC as the name of the token due to how ERC20 tokens are written into the Ethereum blockchain. After repositioning itself as a possible layer-2 solution to Ethereum’s scaling and gas fee woes, the price of MATIC skyrocketed in 2021, as Polygon began to compete with other layer-1 protocols like Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Solana (SOL), Avalance (AVAX), Fantom (FTM) and Luna (RIP) for the loyalty of users and developers pushed away by ETH’s issues.
Why are layer 2 chains necessary?
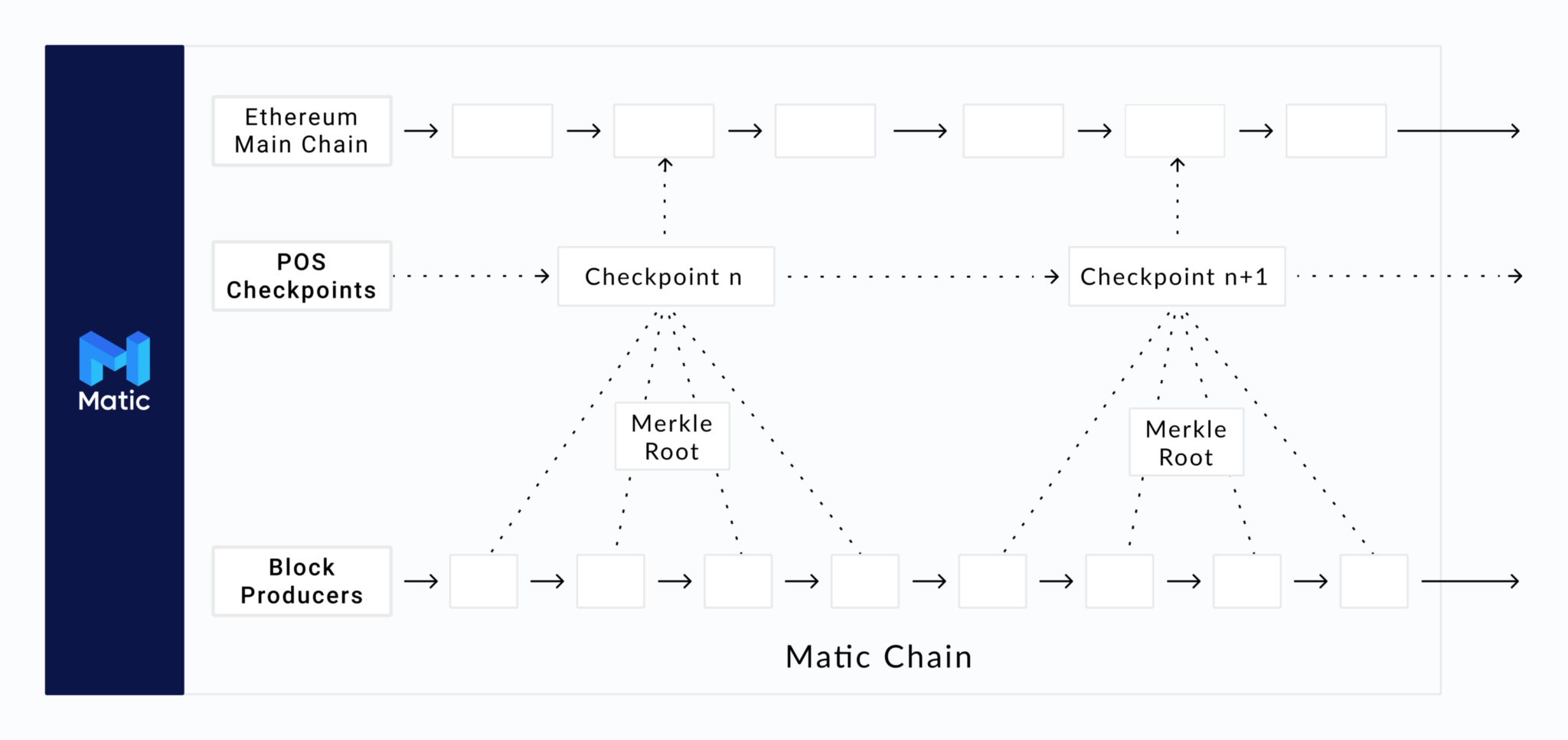
Ethereum is an ideal blockchain due to its level of decentralization, active projects, robust security and strong support by developers and investors, as well as a design that was developed for the smart contracts that power NFT markets, DeFi, and the constantly growing GameFi sector. Unfortunately, Ethereum has a very low TPS compared to other layer-1 blockchains like Polkadot or Solana, so gas fees can sometimes make a transaction inconvenient if it’s too small. Gas fees can increase or decrease wildly depending on the number of transactions coming in, jacking up prices since they all must compete for quicker validation.
The Polygon network avoids the low TPS issue and thus high gas fees by existing parallel to the Ethereum blockchain and acting as a highway for Ethereum or Ethereum-based assets.
How does Polygon work?
Polygon has succeeded as a sidechain to Ethereum by implementing various scaling solutions and incentive structures to keep their network running optimally and efficiently.
A majority of their success comes from using a proof-of-stake (PoS) structure, which if well-supported makes Polygon many times cheaper to use. Being able to conduct cheap transactions allows GameFi and other emerging sectors of crypto to succeed without committing a large amount of capital to move assets.
Validators also exist to allow delegators to stake their tokens to increase the overall speed of block creation, as well as to generate passive income for holders of MATIC tokens.
Originally a simple scaling solution, Polygon now allows developers to launch preset blockchain networks that can be designed to match a client’s desired specifications and needs.
Future of the Polygon ecosystem
In the future, Polygon will support other side chains or enterprise chains that run on their own PoS system, but currently, only secure chains and stand-alone-chains are supported, both of which are MATIC PoS blockchains.
A wide range of blockchain scaling solutions will also be supported to increase transaction throughput while maintaining security and usability. Optimistic Rollups, ZK-Rollups, Validium Chains, and more are already being utilized or expected in the future as the total value locked (TVL) on the Polygon network increases.
Rather than simply act as a highway for transactions, Polygon will become a platform for developers and companies to access a suite of tools compatible with Ethereum. DApps, DeFi protocols, and scalable blockchains will be able to interact with other Ethereum-based projects while still maintaining their own sovereignty, making transactions nearly cost-free and allowing them to securely share information.
How to use Polygon
CoolWallet supports the Polygon chain, allowing you to store MATIC natively and access and trade it via the CoolBitX Crypto App. You can also use the app to connect to DeFi protocols via our MetaMask and Wallet Connect integration.
Ethereum can be bridged to the Polygon network in a few minutes with the correct wallet and some Ether and MATIC ready to be transferred.

DELIVERED EVERY WEEK
Subscribe to our Top Crypto News weekly newsletter
To set up the Polygon network on MetaMask independently, navigate to the network settings of your supported wallet and select “Custom RPC” to begin entering the details of the Polygon network. Enter the following information to begin bridging your assets to Polygon:
Network Name: Polygon Mainnet
New RPC URL: https://rpc-mainnet.maticvigil.com/
Chain ID: 137
Currency symbol: MATIC
Block Explorer URL: https://explorer.matic.network/
After saving the details, your wallet is now able to transfer assets to the Polygon network.
Transferring assets to Polygon
Ethereum and MATIC can now be sent to the Polygon network to trade and interact with dApps, NFT marketplaces, and blockchain games. If your wallet contains zero MATIC, a small amount can be received from https://matic.supply/, a faucet that distributes a little MATIC over time to help users initiate transactions.
Set your wallet’s network back to the Ethereum mainnet, then connect your wallet to the MATIC network website. Your wallet will redirect you to the Polygon bridge, where you can find which asset you would like to move. Transactions take 5-10 minutes, and Ethereum gas fees are applied to the transaction. Your assets can then be viewed on the main page’s web wallet.
Popular dApps such as QuickSwap, a decentralized exchange, and Aave, a lending market, can now be accessed with your digital assets now easily tradable on Polygon, the most popular layer 2 of Ethereum.




