Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)?
- Understanding EVM compatibility
- EVM compatibility vs EVM equivalence
- What are zkEVMs?
- The Importance of EVM-Compatible Blockchains
- Ethereum and the 10 Best EVM-Compatible Chains
- 10 Use Cases of EVM-Compatible Blockchains
- 5 Tips to Safely Use EVM Assets in Cold Storage
- Conclusion
Written by Werner Vermaak
Introduction
Ever wondered why some of your crypto addresses are the same even though they represent assets from different blockchains such as Ethereum, Polygon, and Binance Smart Chain? The answer: EVM.
In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies, an important concept that drives both the market and innovation is that of Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible chains, a class of cryptocurrency networks that share smart contract compatibility. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of EVM-compatible chains and how to securely access them in cold storage with a quality hardware wallet like CoolWallet.
What is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a powerful component of the Ethereum ecosystem. It’s a global, decentralized computer that executes smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. The EVM runs this code and ensures that the outcome is deterministic, meaning that given the same input, the output will always be the same.
Understanding EVM compatibility
Simply explained, EVM compatibility is the ability of a blockchain to write and deploy smart contract code that is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine and can therefore be recognized by the Ethereum network’s nodes.
What are EVM-compatible chains?
EVM-compatible blockchain networks execute smart contracts written in the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) programming language, such as Solidity. These chains replicate or extend the functionality of Ethereum while offering improvements or modifications and push the envelope in the realm of DeFi, pulling billions in total value locked (TVL) from investors.
They maintain compatibility with the EVM, allowing developers to deploy their existing Ethereum smart contracts on these networks. They can either have their own independent main networks, like Binance Smart Chain, Avalanche and Tron’s layer-1 chains, or be a layer-2 network that’s built on top of Ethereum.
Why the need? Well, EVM-compatible chains bring an array of benefits like superior scalability, quick transactions, lower costs, and unique features. They tap into Ethereum’s established ecosystem, allowing developers to reutilize code and interact with prevalent decentralized apps, fostering interoperability and network effects for users.
Chains like Binance Smart Chain, Avalanche, Polygon, Fantom, among others, are notable EVM-compatible examples. They present diverse platforms for creating and launching decentralized apps while capitalizing on Ethereum’s expansive offerings.
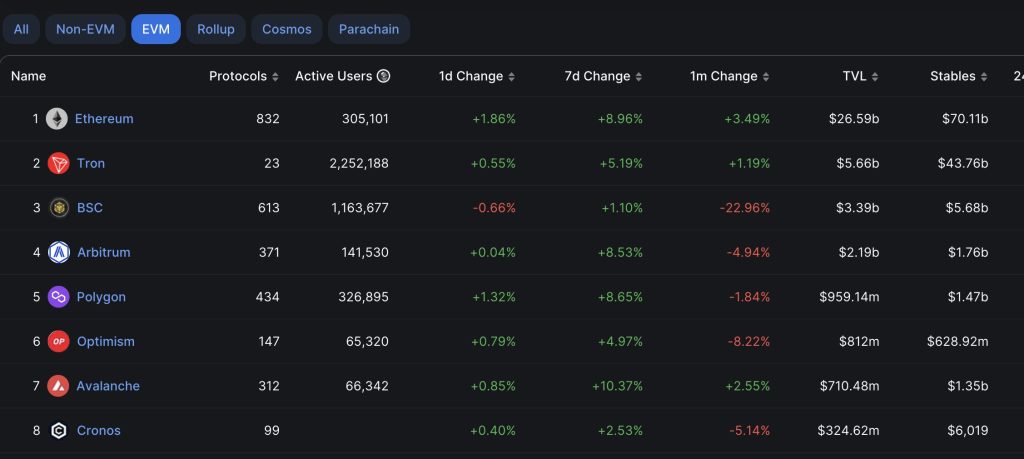
The compatibility accelerates Dapp launches, helping fledgling blockchains to gain momentum in the market. Users, lured by early Dapp testing rewards such as airdrops, and potential high returns from early participation in staking or liquidity pools on new blockchains and DeFi protocols, are more inclined to adopt these chains. EVM compatibility also eases cross-chain fund transfers, a crucial success factor for networks like Binance Smart Chain. It simplifies bridging assets from Ethereum to BSC and others, enhancing user convenience, similar to how city bridges encourage local commerce and revenue generation, fostering a symbiotic environment in the blockchain space.
Let’s review quickly:
EVM stands for Ethereum Virtual Machine. It’s like a global computer where all the transactions and smart contract executions in Ethereum occur.
When a blockchain is “EVM Compatible,” it means that the blockchain is built in a way that it can understand and execute the same instructions as the EVM does. This means that you can write a smart contract for Ethereum, and it will also work on any EVM-compatible chain.
So why would other blockchains want to be EVM-compatible? Here are a few reasons:
- Interoperability: EVM compatibility allows these chains to interact with Ethereum’s ecosystem. Since Ethereum is the largest and most widely used smart contract platform, being able to interact with it gives these other blockchains access to a large user base and established protocols.
- Ease of Use: Since they use the same instructions as Ethereum, developers who already know how to write smart contracts for Ethereum can easily write for EVM-compatible chains. They don’t have to learn a new language or new tools.
- Leverage Existing Applications: Existing Ethereum applications and smart contracts can be ported to these chains with little to no changes. This is an excellent way for these chains to quickly build up a strong set of applications.
However, it’s important to note that while they can run the same code, these EVM-compatible chains may have different performance characteristics, different consensus mechanisms, or different tokenomics. For example, Binance Smart Chain offers faster transaction times and lower fees than Ethereum, but it does so at the cost of decentralization, as it’s controlled by a smaller number of nodes.
So, in summary, EVM-compatible chains are like Ethereum “twins” – they understand and use the same language (Ethereum’s smart contract language) but may have different personalities (different features or compromises).
EVM compatibility vs. EVM equivalence
EVM-equivalent chains are those that have fully implemented the EVM code and are in full compliance with the Ethereum yellow paper. This means that any smart contract that can be run on the Ethereum main net can also be run on an EVM-equivalent chain.
EVM-equivalent chains are typically more expensive to set up and maintain than EVM-compatible chains, but they offer the advantage of complete compatibility with the Ethereum ecosystem.
Meanwhile, EVM-compatible chains are typically forks of the Ethereum blockchain, meaning that they have copied the EVM code and are able to run the same smart contracts. However, there may be some minor differences in the way that EVM-compatible chains implement the EVM, which can lead to compatibility issues. For example, some EVM-compatible chains may have different gas prices or transaction fees, which can affect the way that smart contracts are executed.
Here’s a simpler explanation:
- Think of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) as a gaming console (like an Xbox or PlayStation), and the smart contracts are like the games you play on it.
- “EVM-compatible” chains are like other consoles that can also play these games because they copied the original game system’s design.
- However, just like different consoles might have different controllers or online store prices, EVM-compatible chains might have some small differences, like different “gas prices” or transaction fees, which could change the gaming (or in this case, contract execution) experience slightly.
- “EVM-equivalent” chains, on the other hand, are like an exact replica of the original gaming console. They follow all the original design specs (in Ethereum’s case, the Ethereum Yellow Paper), and therefore can play any game (or run any smart contract) exactly as the original console (Ethereum) does.
- Creating these perfect replicas might cost more, like making an exact clone of Xbox might be more expensive, but the advantage is that you’ll be completely compatible with all the Xbox games and accessories (or in Ethereum’s case, the entire Ethereum ecosystem).
What are zkEVM blockchains?
A lot of hype in 2023 is coming from the zero-knowledge sector. A zkEVM chain is a type of blockchain that uses a zero-knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine (zkEVM) to execute smart contracts. zkEVMs are a type of virtual machine that can verify the correctness of transactions without revealing the underlying data. This makes them ideal for applications that require privacy, such as DeFi and gaming.
zkEVM chains offer a number of big advantages over traditional blockchains, including:
- Scalability: zkEVM chains can process transactions much faster than traditional blockchains because they do not need to store the full state of the blockchain.
- Security: zkEVM chains are very secure, because they use zero-knowledge proofs to verify the correctness of transactions.
- Privacy: zkEVM chains can provide privacy for users, because they do not need to reveal the underlying data of transactions.

DELIVERED EVERY WEEK
Subscribe to our Top Crypto News weekly newsletter
Some of the hottest projects that are developing zkEVM chains include:
- Polygon zkEVM: Polygon zkEVM is a zkEVM chain that is built on top of the Polygon network. It is designed to be fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), so that developers can easily port their existing Ethereum applications to Polygon zkEVM.
- zkSync: zkSync is a zkEVM chain that is being developed by Matter Labs. It is designed to be very scalable and secure, and it is expected to be one of the most popular zkEVM chains in the future.
- StarkNet: StarkNet is a zkEVM chain that is being developed by StarkWare. It is designed to be very scalable and private, and it is already being used by a number of DeFi projects.
The Importance of EVM-Compatible Blockchains
EVM compatibility is crucial as it allows developers to leverage the extensive Ethereum ecosystem without having to rewrite their applications for different blockchains. This means:
- Familiarity and Interoperability: Developers familiar with Ethereum can easily build on EVM-compatible chains, reducing the learning curve. These chains can also interact with Ethereum, fostering an interconnected ecosystem.
- Flexibility and Customization: EVM-compatible chains offer the flexibility to customize the blockchain’s parameters, such as block time and transaction fees, to suit specific use cases.
- Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness: Some EVM-compatible chains offer higher scalability and lower transaction costs than Ethereum, making them attractive alternatives.
- Early Adoption Opportunities: For crypto owners, early adoption of these chains can present lucrative opportunities, much like the early days of Ethereum.
- Interconnected Ecosystem: EVM-compatible chains contribute to a more interconnected and interoperable blockchain ecosystem, enhancing the overall value proposition of blockchain technology.
Ethereum and the 10 Best EVM-Compatible Chains
Let’s explore some of the most prominent EVM-compatible blockchains. All of them are supported natively by CoolWallet Pro and CoolWallet App:
- Ethereum (ETH): The pioneer of smart contracts and dApps, Ethereum is the standard for EVM-compatible chains.
- Binance Smart Chain (BSC): Known for its low transaction fees and high performance, BSC has attracted a significant number of dApps and users.
- Polygon (MATIC): Polygon is a layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, aiming to provide faster and cheaper transactions.
- Avalanche C-Chain: A smart-contract-enabled platform within Avalanche, ensuring Ethereum compatibility while providing high throughput and scalability.
- OKX Chain: A proprietary blockchain network by OKX Exchange, promoting decentralization while enhancing security, performance, and asset management.
- Arbitrum: A Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, which boosts transaction throughput and reduces cost by optimizing on-chain data.
- Optimism: A Layer 2 scaling solution using Optimistic Rollup technology, enhancing Ethereum’s scalability by reducing transaction costs and time.
- Chronos: A high-speed cross-chain interoperability layer developed by Crypto.com, allowing seamless transfers and smart contract operations across different blockchains.
- Cardano: Although not natively EVM-compatible, Cardano is working on a project called KEVM, which will allow it to run Ethereum-style smart contracts. Cardano, started by Ethereum co-founder Charles Hoskinson, was originally an ERC20 token that moved to its own main net in 2019.
- TRON (TRX): TRON is a high-throughput blockchain that aims to decentralize the internet. It is EVM-compatible and has a large and active user base. It started life as an ERC-20 token.
- ThunderCore (TT): ThunderCore is a high-performance, EVM-compatible Web3-focused gaming blockchain with its own native currency, Thunder Token (TT) and a cross-chain mechanism called ThunderCore Bridge.
10 Use Cases of EVM-Compatible Blockchains
EVM-compatible blockchains have a wide range of use cases. Here are a few of the most promising:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
DeFi applications are the most common use case, providing services like lending, borrowing, and yield farming. - NFT Marketplaces:
These blockchains host various NFTmarketplaces, enabling the creation, buying, and selling of NFTs, often at very low transaction fees which makes trading them easy and effortless. - Gaming and Virtual Worlds:
EVM-compatible chains are increasingly being used to build blockchain-based games and virtual worlds. - Supply Chain and Traceability:
Blockchain’s immutable nature makes it ideal for supply chain management, ensuring product authenticity and traceability. - Governance and DAOs:
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) use these blockchains for transparent and democratic decision-making processes. - Tokenization and Crowdfunding:
EVM-compatible chains facilitate the tokenization of assets and crowdfunding for projects. - Interoperability and Cross-Chain Bridges:
These chains enable the seamless transfer of assets between different blockchains. - Decentralized Identity (DiD):
Blockchain-based identity solutions provide a secure and privacy-preserving way of managing digital identities. - Social Media and Content Platforms:
Some platforms leverage these chains to create decentralized social media and content platforms, providing users with more control over their data. - Supply Chain Finance:
Blockchain can streamline supply chain finance by automating processes and increasing transparency.
5 Tips to Safely Use EVM Assets in Cold Storage
If you’re serious about keeping your crypto portfolio as safe as possible against the threats of hacks, scams, and custodial negligence, you’ll know by now that cold storage—storing cryptocurrencies offline—is the way to go.
Things are pretty straightforward with a hardware wallet. This custom device, usually in a USB drive or card format, locks your private key away in a secure element (make sure your wallet has one, a minimum of EAL5+ is recommended) so no one can access it, and also requires physical confirmation for any transaction to execute.
Here are 5 top tips to safely access different EVM chains in cold storage:
- Choose a trusted wallet brand:
Ensure that the cold wallet you choose supports the EVM-compatible chain you want to access and that it has a proven security track record and high-quality customer support. This is essential to ensure there are no code backdoors or manufacturing supply chain attacks that can compromise your whole portfolio. CoolWallet has recently announced it will make its open-source EAL6+ secure element’s code public for the sake of full transparency, following the recent Ledger Recover controversy. - Secure your recovery seed:
Any good cold wallet should permanently lock your private key in its chip so that no one, not even you, can access it. Your recovery seed helps you regain access to your assets if you lose your wallet or connecting device. Keep it offline and in a secure place, away from exposure to anyone but you. - Regularly update your wallet:
Keep your wallet software up-to-date to ensure you have the latest security features. Hackers may modify outdated versions and try to phish you to compromise your security. - Verify transactions:
Always verify the details of your transactions before confirming, especially when interacting with smart contracts. CoolWallet’s new partnership with Web3 security firm KEKKAI provides real-time analytics and protection for your Dapp transactions.
Conclusion
EVM-compatible chains offer a world of possibilities for developers and crypto owners alike. Together with layer-2 networks, they extend the reach of Ethereum’s robust ecosystem, offer scalability solutions, and provide unique opportunities for early adopters.
These chains also serve as a failsafe in case anything happens to the Ethereum network, and often boast incredibly fast transaction speeds and ultra-low gas fees, which makes them a great alternative in times when the Ethereum network is congested and expensive.
However, keep in mind that these EVM chains are not Ethereum and that there can other issues such as early investors dumping, greater centralization (which can result in a 51% attack or market manipulation), poor tokenomics and emissions through staking, as well as a lack of a strong community that could see them fade into obscurity over time.
As the blockchain space continues to evolve, these EVM-compatible chains will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping its future.
Keep your EVM chain coins in the safest and most convenient cold storage available with your CoolWallet Pro.




